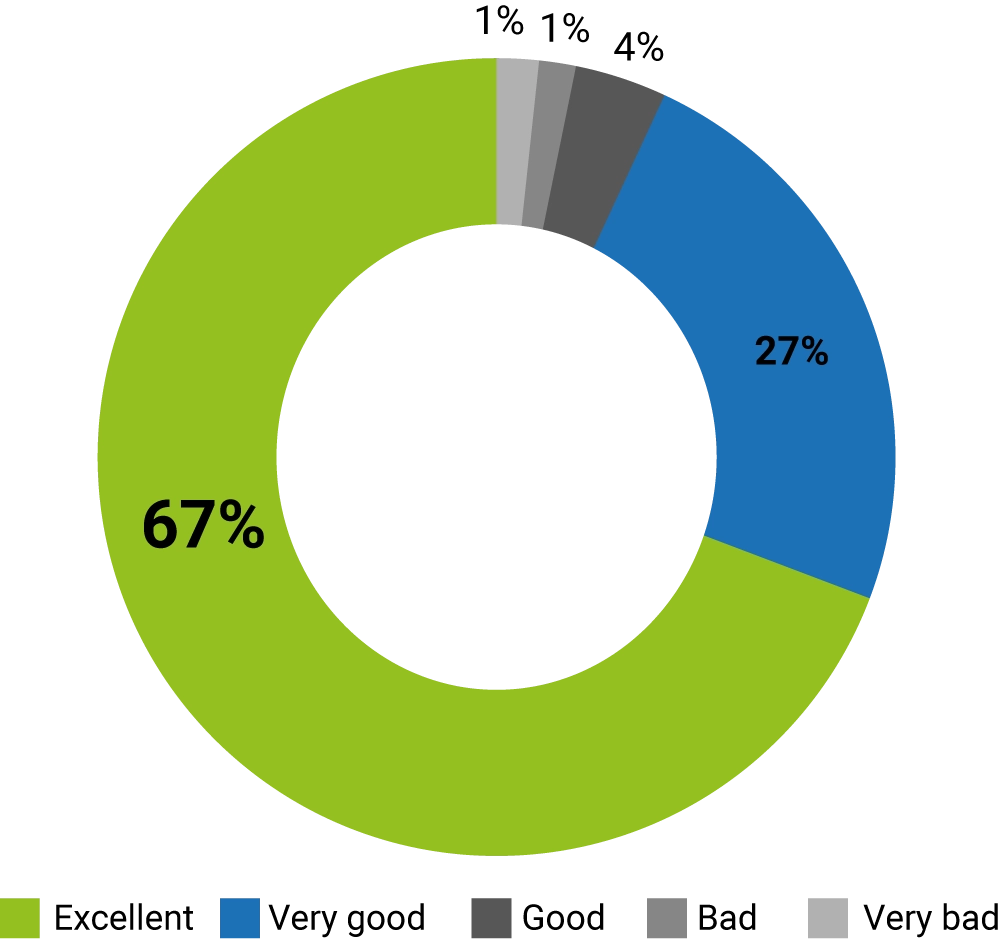
Overview: The Industrial Metaverse
During my job at a Global Automotive OEM, I served as the sole Designer responsible for the UX strategy for their immersive training ecosystem. The main goal was to use Virtual Reality (VR) to train assembly line operators on unreleased vehicle models using simulations. This approach advanced the training timeline by months, allowing operators to learn assembly processes before the first physical prototype was built, drastically reducing time-to-market.
The Challenge: The Digital Gap
Implementing VR in a factory setting presented a unique friction point: the target users were specialized operators, often with low digital affinity and limited gaming experience. The main area to improve was usability, since the existing system used resulted in:
- Cognitive Overload: Complex inputs led to frustration where the existing gaming interaction models failed to align with the operators' industrial mental models.
- Physical Strain: The existing interaction method often required operators to hold their arms up for extended periods to read instructions, leading to fatigue.
- Perception: The exisiting design was perceived as unpleasant, which, combined with poor interaction ergonomics, resulted in low perceived quality.
Methodology: Contextual Research in the Immersive Environment
To build a tool that operators would actually adopt, I applied rigorous UX methodologies adapted for 3D environments, grounding the redesign in observed operator behavior and ergonomic realities:
- Contextual Inquiry: Conducted ethnographic studies by observing operator behavior during VR training sessions. This allowed me to understand the ergonomic constrains and mental models as they interacted with the digital prototypes.
- Prototyping Strategy: Moved from paper sketches to Adobe XD for creating spatial mockups and defining the UI logic/flow. This was essential for visualizing the layout and testing UI placement and readability in 2D before being implemented in the VR engine.
- Dev Collaboration: Worked daily with Game Developers (Unity) to ensure design feasibility and accurate implementation of the interaction logic.
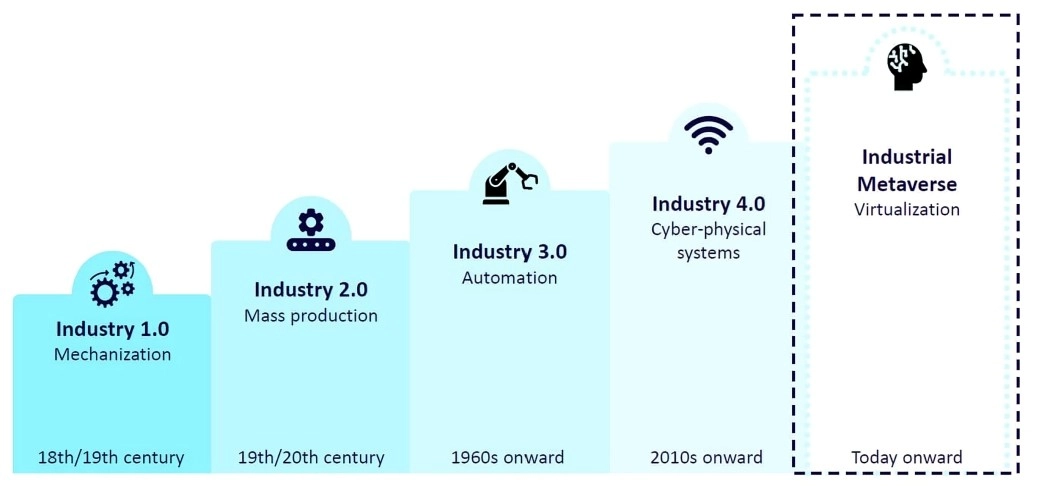
Solution: Spatial UX Redesign and Touch Environment Interaction
The core of the solution was the redesign of the fundamental interaction model to eliminate physical strain and cognitive friction while improving visual aesthetics using:
- UI Design Simplification: The design prioritized a Task-Oriented visual approach that maintained corporate seriousness while eliminating a "gaming" aesthetic. This involved removing superfluous elements, utilizing a simple and clear font, and enabling a larger interactable area to ensure better precision and overall usability in the virtual environment.
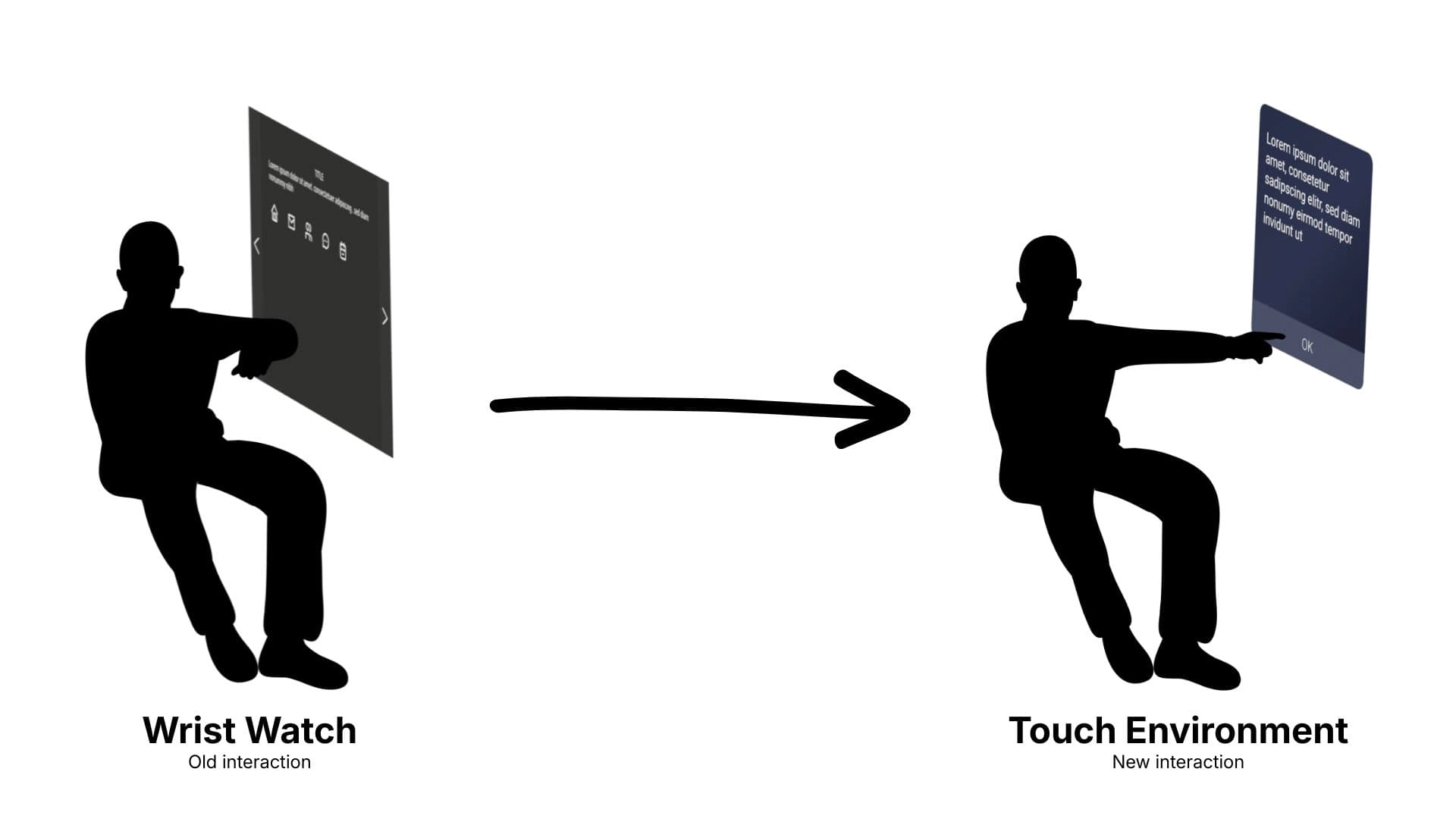
- Touch Environment Interaction: We replaced the demanding "Wrist Watch Interaction" with a new system where the information poster became a static element of the environment. This allows the user to simply reach out to interact, mirroring real-world behaviour and eliminating the need to hold their arm up for extended periods to read assembly instructions.
- Development Guidance (Unity): Created clear development guidelines for Unity developers to ensure accurate and consistent implementation of the new interaction and design across the system, unifiying styles.
- New Movement System (Teleportation): A new in-game movement system (teleportation) was designed and introduced to mitigate motion sickness and improve overall user comfort within the virtual environment.
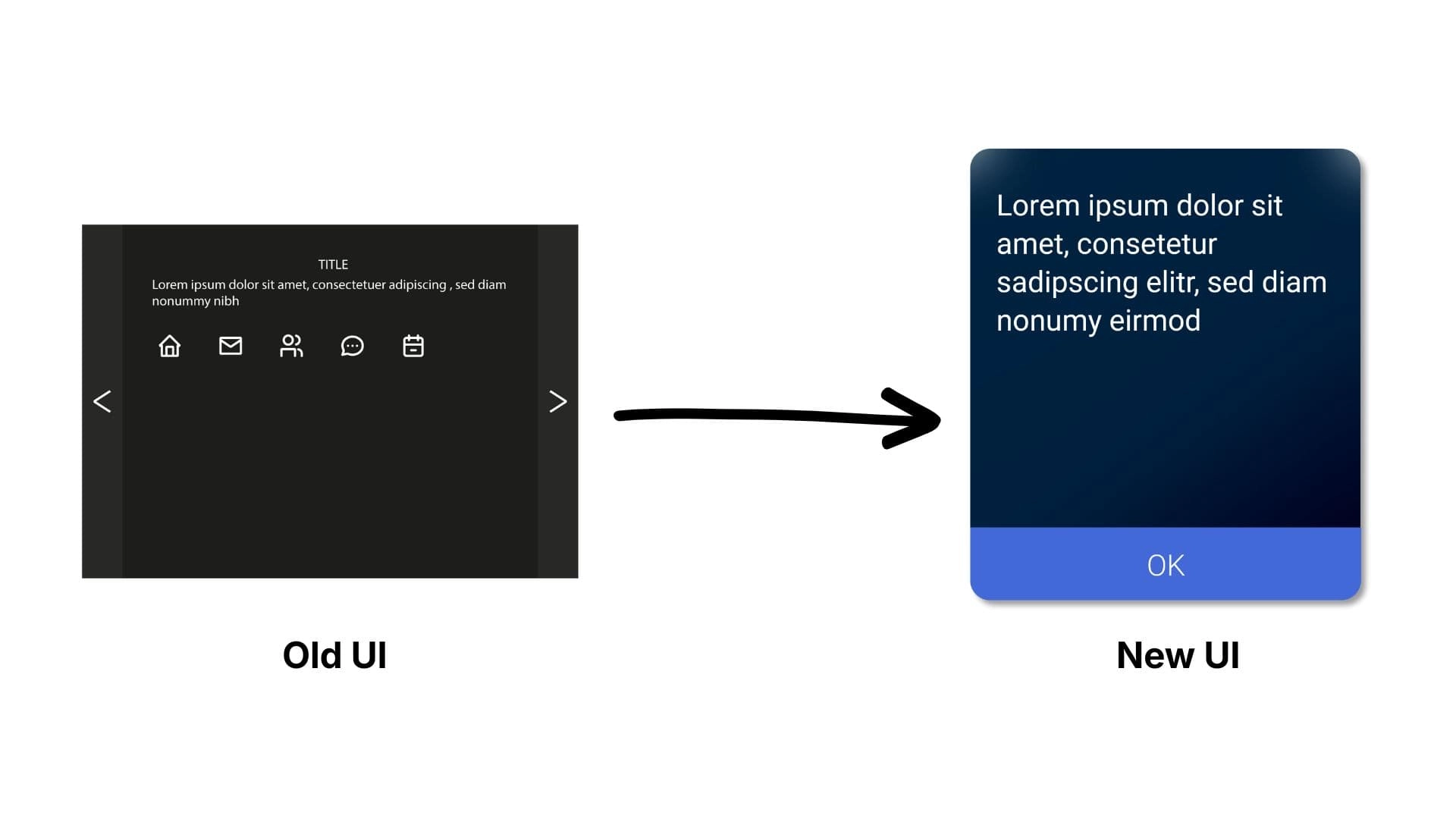

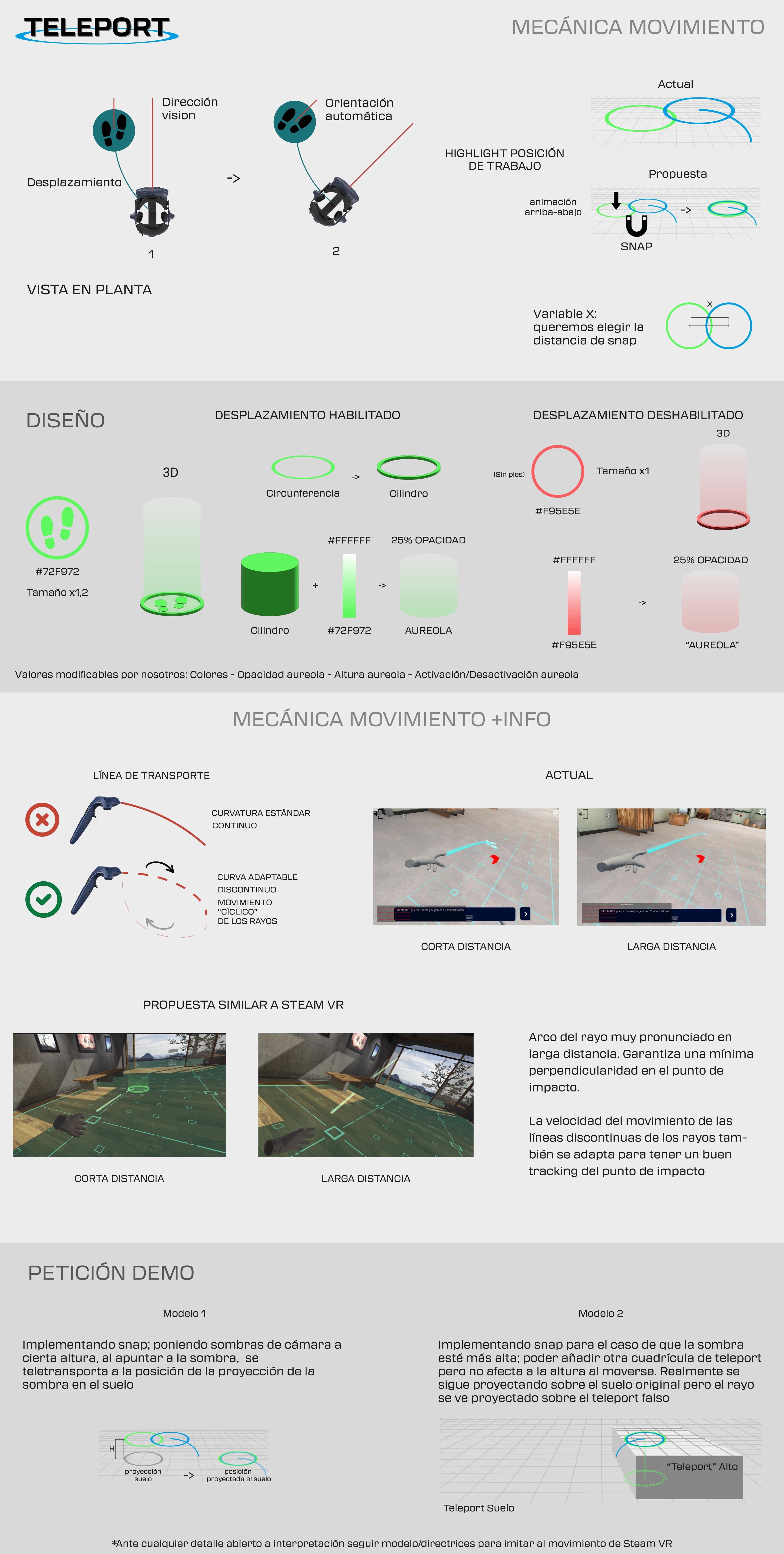
Validation & Impact
The new interaction system was validated through rigorous testing sessions. The new interface significantly reduced the learning curve for new operators as well as being welcomed by existing users.
94%
Positive Feedback
Combining "Excellent" (67%) and "Very Good" (27%) ratings regarding the new interaction system and button design.
~100
Operators Surveyed
Validation data collected from factory employees across different shifts and experience levels.